However, China’s import and export of automotive products (including auto parts, excluding motorcycles, the same below) are very much disfavored. The import and export volume of automotive products accounted for a very small proportion of total imports and exports in China (up to 3.80% and 2.01% respectively), and they have long been in a trade deficit. Our previous analysis shows that the proportion of China's auto vehicles (especially passenger cars) is still at the lowest level in the world. At the same time, in China's major export industries, the export volume of automotive products also ranks at the end of each manufacturing industry. The following is the detailed content.
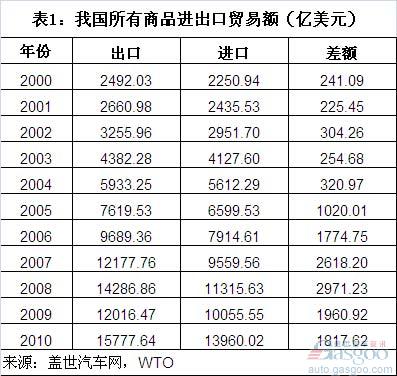
The proportion of auto goods in China’s total import and export volume is still slightly based on the WTO data compiled by Gasgoo. In 2000, the total import and export volume of various commodities in China was 225.094 billion U.S. dollars and 249.203 billion U.S. dollars, respectively. It only increased 8.20% and 6.78% to US$243.553 billion and US$266.98 billion. In December 2001, China formally joined the WTO. In the following nine years, the compound annual growth rate of imports and exports reached 21.41% and 21.87% respectively. In 2010, China’s total imports and exports reached US$139.90 billion and US$1.577764 trillion, respectively.
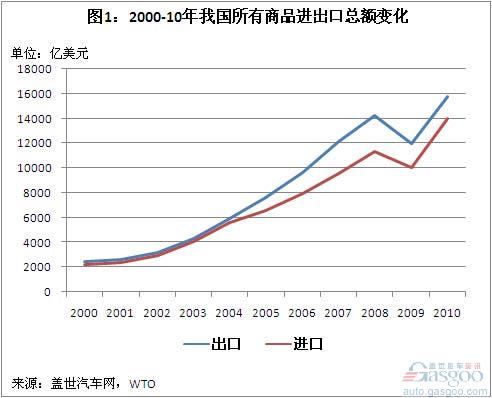
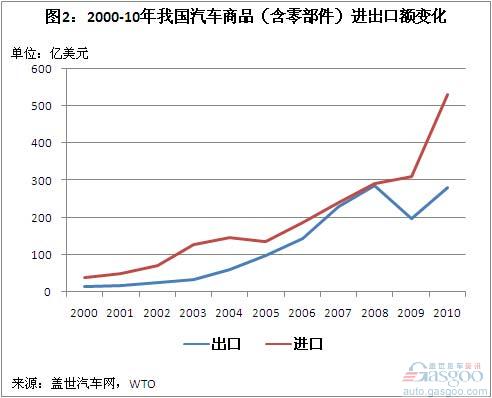
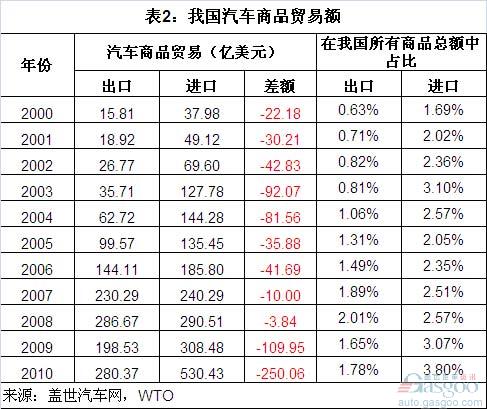
In 2000, the total import and export of automobile products in China was 3.798 billion U.S. dollars and 1.581 billion U.S. dollars, respectively, which accounted for only 1.69% and 0.63% of the total imports and exports of China. After that, the total volume of auto goods trade showed an upward trend (except for 2009). In 2010, the total import and export volume of automotive goods reached US$ 53.043 billion and US$ 28.037 billion, respectively.
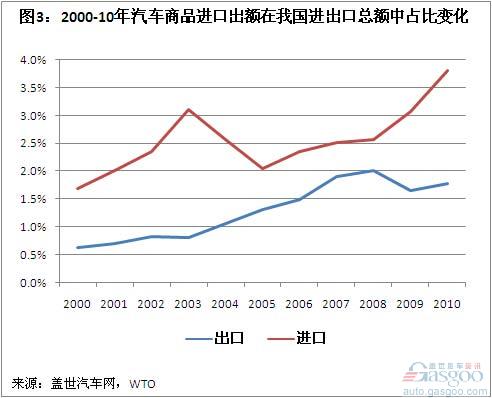
Its share in China’s total import and export volume has also been on the rise, but it is still very small. In 2010, the proportion of imports of auto goods in China’s total imports of all goods rose to 3.80%, the highest level since the 21st century; the proportion of auto exports rose to 1.78% in that year, but its highest level appeared in 2008 – It reaches 2.01%.
The deficit of auto goods against the European Union and Japan and South Korea to the US surplus From 2000 to 2010, China's overall import and export trade was in a surplus (although from 2009 onwards, the surplus was significantly reduced). However, China’s auto commodity trade has been at a deficit since at least 2000. In 2000-02, China's auto trade deficit increased gradually, but it was generally in the range of $2.2 billion to $4.3 billion. In 2003, the trade deficit jumped to US$9.207 billion. Although it decreased slightly in 2004, it was still above US$8.1 billion. In 2005-06, it fell back to 3.5-4.2 billion U.S. dollars. In 2007, the trade deficit dropped to US$1 billion, and in 2008 it narrowed to US$384 million.
However, in 2009, the deficit in auto goods trade increased dramatically to 10.995 billion U.S. dollars, and in 2010 it further increased to 25.006 billion U.S. dollars.
The major trading countries of China's auto products are the European Union, the United States, Japan, and South Korea. From 2000 to 2010, the import and export trade volume with these four regions/countries accounted for 76.9% of the total value of China's auto commodity trade. Among them, the EU, Japan, and South Korea (especially the former two) are the major import sources of China's automotive products. From 2000 to 2010, China has accumulatively imported 91.798 billion U.S. dollars of automotive products from the European Union, imported 72.796 billion U.S. dollars of automotive products from Japan, and imported 19.815 billion U.S. dollars of automotive products from South Korea.
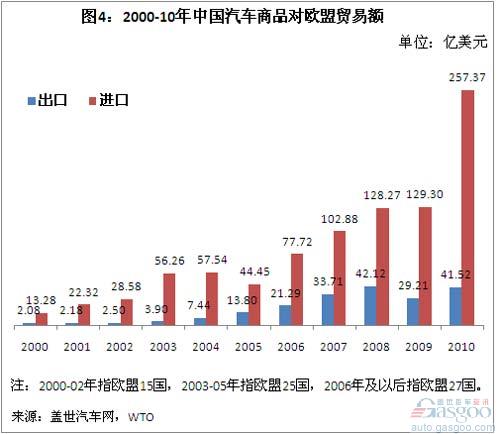
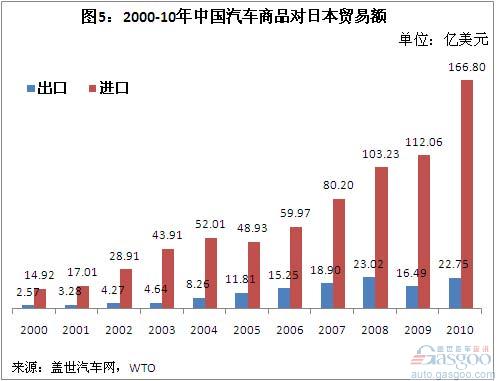
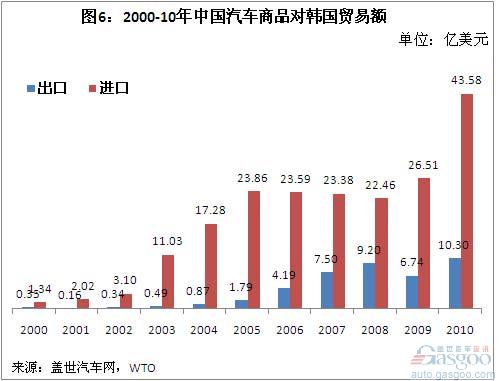
In this 11-year period, China's auto trade with the European Union, Japan, and South Korea both suffered a deficit. In 2009, China’s auto trade deficit with the European Union reached US$10.001 billion. In 2010, the trade deficit doubled to US$21.586 billion. The trade deficit with Japan reached US$95.57 billion in 2009 and increased to US$14.405 billion in 2010. The trade deficit in 2010 also reached US$3.328 billion.
Note:
When the WTO published its 2002 data, it listed the data for the previous two years. The WTO's import and export data for "China", "Hong Kong, China" and "China Taiwan" are listed separately. This article uses the "China" data listed. WTO lists China’s trade data on the “EUâ€, 2000-02 refers to the EU-15 countries, 2003-05 refers to the EU-25 countries, and 2006 and later refers to the EU-27 countries.
Nantong Jinchao Machinery Co., Ltd. , https://www.ntjinzhaomachine.com
