Photosynthetically active radiation is the part of solar radiation that can be used for photosynthesis by green plants. Abbreviation is PAR, the acronym for photosynthetically active radiation. Photosynthetically active radiation is the basic energy source for biomass, which directly affects the plant's growth, development, yield, and product quality. PAR has three types of metering systems: 1. An optical system, measured in illuminance (lx). This system is based on the human eye's response to brightness; 2. The energetic system is measured by the radiant flux density (Wm-2) within a certain characteristic wavelength range, ie the photosynthetic effective wavelength band; The system is measured by the photon flux density (umol m-2 s-1).
In addition, let us look at the explanation of the two kinds of photosynthetically active radiation.
Explanation of "photosynthetically active radiation" in the reference book:
1. The ratio of the radiant energy that can be used by tea plants to the total solar radiation energy. Solar radiant energy is a general term. Its wavelength range is from 310 to 2300 nm, but tea trees can absorb only the wavelength of 380 to 710 nm (ie, visible light). Therefore, in fact, tea can only use the total radiant energy that falls to the ground. About half of this value can represent photosynthetically active radiation.
2, the wavelength of about 380 ~ 720 nm, can be absorbed by the green plant chlorophyll, and participate in the photochemical reaction of solar radiation spectrum. The spectral range of photosynthetically active radiation is 380 to 710 nm in Eastern European countries and 400 to 700 nm in Western Europe and the United States. Photosynthetically active radiation is composed of direct radiation and scattered radiation in the above spectral range. When calculating the total amount of photosynthetically active radiation or the total amount of monthly total, it can be obtained from the simple formula of X Modau: Q=0.43S′+0.57D.
Explanation of "photosynthetically active radiation" in academic literature:
1. Photosynthetically active radiation refers to the portion of solar energy that enables crop chloroplasts to utilize and carry out photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the fixation of CO2 by crops to produce dry matter under light energy.
2. In the process of photosynthesis, plants mainly assimilate the visible light energy with a wavelength of 400-700nm, which accounts for about half of the total radiation, and are called photosynthetically effective radiation. It is the solar radiation during the growth period that is directly related to the plants.
3. The part of the energy (400-700nm) that the green plants use for photosynthesis is called photosynthetically active radiation. Here we used HEIFE during the 1990-1991 FOP in Linze and in May and June 1992 BOP in Zhangye. Obtained PAR Observation Data to Analyze and Study Characteristics of Photosynthetically Active Radiation in Arid Region of Luzhou
4, also known as photosynthetically active radiation. In the waters of Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake, the visible light intensity on the water surface is on the order of 10-1μE·m-2·s-1, and the light intensity at 0.5m is 10-2μE. M-2・s-1 order of magnitude (Figure 5, the average of 3 measurements)
5. The mid-wavelength of solar radiation is in the range of 04 to 07 μm. The part of solar radiation that can be used for photosynthesis by green plants is called photosynthetically active radiation.
6, solar radiation is a continuous spectrum, but the chloroplast can only absorb visible light of 0.38μm ~ 0.71μm for photosynthesis This area of ​​solar radiation known as photosynthetically active radiation
In the table below, we have listed some data of different ecological factors in the evergreen broad-leaved forest under different light conditions. In order to allow people to read the daily averages of ecological factors in different environments more clearly, I will do some analysis.

Diurnal changes of ecological factors such as temperature, relative humidity, surface temperature, and photosynthetically active radiation under different light conditions
From the above figure, it can be seen that the surface temperature and photosynthetically active radiation of the air temperature in the ore are higher than those of the window and understory during each measurement period of the day. The photosynthetically active radiation also had significant differences under different light conditions (p<0.05). The photosynthetically active radiation in the depression was significantly greater at the time of day than at the forest window and under the forest, and the photosynthetically active radiation at the depression was at 12:00. The maximum point is about 1800μmol.m -2.s -1, and the maximum photosynthetically active radiation of the forest window is the highest around 13:00, which is about 1300μmol.m -2.s -1t. Understory light environment is affected by With the effect of light spots, photosynthetically active radiation changes frequently during the day, but their values ​​are below 100 μmol.m -2 .s -1 .
Daily mean values ​​of ecological factors in different light environments
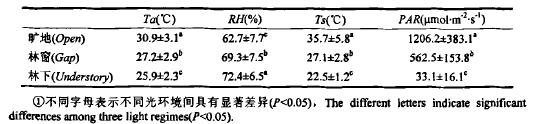
From the above table, the daily mean values ​​of the four main ecological factors have significant differences under different light conditions (p<0.05). The average daily temperature of the mine is higher than the forest window and understory, and the daily average surface temperature and photosynthetically active radiation are significantly higher than the forest window and understory, and the daily average photosynthetically active radiation is 2.1 and 36.4 times of the forest window and understory respectively.
Camping Chair,Foldable Camping Chair,Folding Camping Chair,Camping Legless Chair
Wuyi Superior Leisure Products CO.LTD , https://www.easytcsuperior.com
