The "Guidelines for Quantitative Risk Assessment for Chemical Enterprises", "Technical Conditions and Testing Methods for Ammonia Detection and Alarming Devices," and "Deflosion Safety Release Standards" drafted by the Qingdao Institute of Safety Engineering, China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation, organized by the State Administration of Work Safety. The "Standards for the Safety Management of Hazardous Chemicals Construction Projects", "Safety Regulations for Ethanol Gasoline" and "Standards for Equipped Emergency Relief Supplies for Dangerous Chemicals Units" were issued on December 21 for comments from various places. Experts believe that the promulgation and implementation of the standard will completely change the situation in the quantitative risk assessment of the chemical industry in China for a long time without uniform standards, and chemical safety evaluation will tend to be reasonable and standardized.
Among them, the “Guidelines for Quantitative Risk Assessment of Chemical Enterprises†stipulates the technical requirements in the quantitative risk assessment process of chemical companies, and is applicable to the quantitative risk assessment of newly built, rebuilt, expanded, and in-service installations (facilities) of onshore chemical companies.
It is understood that quantitative risk assessment is to identify and quantify hazards, make comprehensive and comprehensive analysis, and use the data and conclusions obtained from quantitative risk assessment, and comprehensively consider economic, environmental, reliability, and safety factors. Appropriate risk management procedures and measures are a working method to provide technical support for design, operation, safety management and decision-making. At present, the United States, Britain, and the Netherlands have formulated specific guidelines for quantitative risk assessment that suit their own national conditions and are widely used.
According to Zhang Haifeng, one of the main drafters of the standard, in recent years, quantitative risk assessment technology has been used in a large number of applications in the domestic petrochemical industry. For example, the Safety Engineering Research Institute of Sinopec has successively conducted risk assessment of Yantai Wanhua phosgene project and Shanghai Chemical Industry Park risk assessment. Quantitative risk assessments such as the risk assessment of LNG receiving stations in Macao; PetroChina conducted evaluations of projects such as the “Quantitative Risk Assessment of Terminal Projects for China Petroleum Tangshan LNG Projectsâ€; CNOOC conducted quantitative risks for major projects at LNG receiving stations and offshore platforms. Evaluation. However, compared with foreign countries, China does not have quantitative risk assessment criteria and a comprehensive guideline for quantitative risk assessment. It is not standardized in data collection, hazard identification, unit selection, accident model, and risk measurement. How to choose a hazard source? There is no uniform standard for the device, the division of the leakage segment, the model, and the determination of the leakage frequency.
For example, data collection needs to regulate the data types, collection principles and standards of quantitative risk assessment, such as population mobility factors, population boundary range, principle of estimating population, identification of ignition sources, and different types of ignition sources such as points and lines. Type, surface type ignition probability, etc. At the present stage, the data collection of various evaluation items is not standardized and incomplete, and there are erroneous data sources.
Gao Ying Cao Ying of the Fujian Provincial Labor Protection Research Institute told the reporter that because the country does not currently regulate quantitative risk assessment and chemical safety management, the various quantitative assessment methods used by safety assessment agencies in the safety evaluation of chemical construction projects are varied and calculated. The evaluation results are far apart; different evaluation staff use the same method if the values ​​are different, the calculation results are also very different; some chemical products can only use foreign data due to the lack of dangerous parameters, and individual chemical products can only find the dangerous parameters. In the near future, in addition, the contents of safety management at each stage of the chemical construction project are not uniform, and the evaluation personnel can only propose safety management measures according to their own depth of knowledge and understanding of national safety production laws and regulations, thus affecting the safety evaluation of chemical construction projects. Results and quality.
“Evaluation device or unit division needs to be standardized.†Zhang Haifeng analyzed that “the risk of the system is often determined by only a few units. To avoid excessive calculation, it is necessary to select a certain screening method to have a greater impact on the entire system and the risk is relatively high. High units perform risk calculations, which require hazard identification, and systematic analysis methods are used to identify hazards in the assessment area to determine which flammable, explosive, active and toxic substances present major accident risks, and which process failures or errors are likely to occur. Unusual situation and major accident risk."
“In addition, risk metrics and risk criteria also need to be unified. The core content of quantitative risk assessment is to evaluate individual and social risks in the region, draw individual risk contours and social risk curves. Risk criteria are used to determine whether the risk is acceptable. And the criteria for judging the importance of risk. At present, there is no uniform chemical industry recommended risk criteria, recommending a reasonable and acceptable acceptable risk criteria is extremely necessary.†Zhang Haifeng said.
Experts believe that the promulgation and implementation of the "Guidelines for Quantitative Risk Assessment of Chemical Enterprises" and "Standards for the Provision of Emergency Rescue Materials for Hazardous Chemical Units" will help the results of the safety risk assessment of chemical construction projects be more reasonable and effective, thus increasing the The safety of the system will play an important role in regulating chemical safety evaluation and improving the quality of safety evaluation reports.
 Application areas are almost limitless. Usually, a laboratory hydraulic press will be used to prepare samples for analysis by compressing them into pellets or thin films. The particles are forced together, creating a homogenous sample ideal for spectroscopic examination.
Application areas are almost limitless. Usually, a laboratory hydraulic press will be used to prepare samples for analysis by compressing them into pellets or thin films. The particles are forced together, creating a homogenous sample ideal for spectroscopic examination.
Among them, the “Guidelines for Quantitative Risk Assessment of Chemical Enterprises†stipulates the technical requirements in the quantitative risk assessment process of chemical companies, and is applicable to the quantitative risk assessment of newly built, rebuilt, expanded, and in-service installations (facilities) of onshore chemical companies.
It is understood that quantitative risk assessment is to identify and quantify hazards, make comprehensive and comprehensive analysis, and use the data and conclusions obtained from quantitative risk assessment, and comprehensively consider economic, environmental, reliability, and safety factors. Appropriate risk management procedures and measures are a working method to provide technical support for design, operation, safety management and decision-making. At present, the United States, Britain, and the Netherlands have formulated specific guidelines for quantitative risk assessment that suit their own national conditions and are widely used.
According to Zhang Haifeng, one of the main drafters of the standard, in recent years, quantitative risk assessment technology has been used in a large number of applications in the domestic petrochemical industry. For example, the Safety Engineering Research Institute of Sinopec has successively conducted risk assessment of Yantai Wanhua phosgene project and Shanghai Chemical Industry Park risk assessment. Quantitative risk assessments such as the risk assessment of LNG receiving stations in Macao; PetroChina conducted evaluations of projects such as the “Quantitative Risk Assessment of Terminal Projects for China Petroleum Tangshan LNG Projectsâ€; CNOOC conducted quantitative risks for major projects at LNG receiving stations and offshore platforms. Evaluation. However, compared with foreign countries, China does not have quantitative risk assessment criteria and a comprehensive guideline for quantitative risk assessment. It is not standardized in data collection, hazard identification, unit selection, accident model, and risk measurement. How to choose a hazard source? There is no uniform standard for the device, the division of the leakage segment, the model, and the determination of the leakage frequency.
For example, data collection needs to regulate the data types, collection principles and standards of quantitative risk assessment, such as population mobility factors, population boundary range, principle of estimating population, identification of ignition sources, and different types of ignition sources such as points and lines. Type, surface type ignition probability, etc. At the present stage, the data collection of various evaluation items is not standardized and incomplete, and there are erroneous data sources.
Gao Ying Cao Ying of the Fujian Provincial Labor Protection Research Institute told the reporter that because the country does not currently regulate quantitative risk assessment and chemical safety management, the various quantitative assessment methods used by safety assessment agencies in the safety evaluation of chemical construction projects are varied and calculated. The evaluation results are far apart; different evaluation staff use the same method if the values ​​are different, the calculation results are also very different; some chemical products can only use foreign data due to the lack of dangerous parameters, and individual chemical products can only find the dangerous parameters. In the near future, in addition, the contents of safety management at each stage of the chemical construction project are not uniform, and the evaluation personnel can only propose safety management measures according to their own depth of knowledge and understanding of national safety production laws and regulations, thus affecting the safety evaluation of chemical construction projects. Results and quality.
“Evaluation device or unit division needs to be standardized.†Zhang Haifeng analyzed that “the risk of the system is often determined by only a few units. To avoid excessive calculation, it is necessary to select a certain screening method to have a greater impact on the entire system and the risk is relatively high. High units perform risk calculations, which require hazard identification, and systematic analysis methods are used to identify hazards in the assessment area to determine which flammable, explosive, active and toxic substances present major accident risks, and which process failures or errors are likely to occur. Unusual situation and major accident risk."
“In addition, risk metrics and risk criteria also need to be unified. The core content of quantitative risk assessment is to evaluate individual and social risks in the region, draw individual risk contours and social risk curves. Risk criteria are used to determine whether the risk is acceptable. And the criteria for judging the importance of risk. At present, there is no uniform chemical industry recommended risk criteria, recommending a reasonable and acceptable acceptable risk criteria is extremely necessary.†Zhang Haifeng said.
Experts believe that the promulgation and implementation of the "Guidelines for Quantitative Risk Assessment of Chemical Enterprises" and "Standards for the Provision of Emergency Rescue Materials for Hazardous Chemical Units" will help the results of the safety risk assessment of chemical construction projects be more reasonable and effective, thus increasing the The safety of the system will play an important role in regulating chemical safety evaluation and improving the quality of safety evaluation reports.
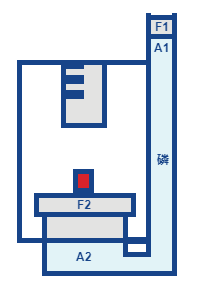
How does a hydraulic press work? Pascal's Law in action
In a hydraulic press, a modest mechanical force (F1) is applied to a small area (A1). As the fluid is moved in one location, it inevitably moves elsewhere within that channel. Then a larger area (A2) generates a magnified mechanical force (F2). The force is transmitted via hydraulic pressure generated by the initial effort, F1.

Hydraulic Press Machine,Shop Press,Hydraulic Press For Sale,Workshop Press
Jiangsu Hoston Machine Tools Co., Ltd. , https://www.haostonmachinetools.com
