I. Introduction
A laser cutting machine, as a kind of equipment, utilizes high-power density laser beams to cut, engrave, and punch. Its working principle is that the laser beams generated by the generator irradiate the surface of workpieces to melt, evaporate, and burn the material's surface layer.
At the same time, after the high-pressure gas blows away the molten material, the cutting is finished.
Laser-cutting technology has been widely applied in metal processing, electronic fabrication, the automotive industry, aerospace and advertising, possessing advantages of high speed, accuracy, narrow slits and small heat-affected zones.
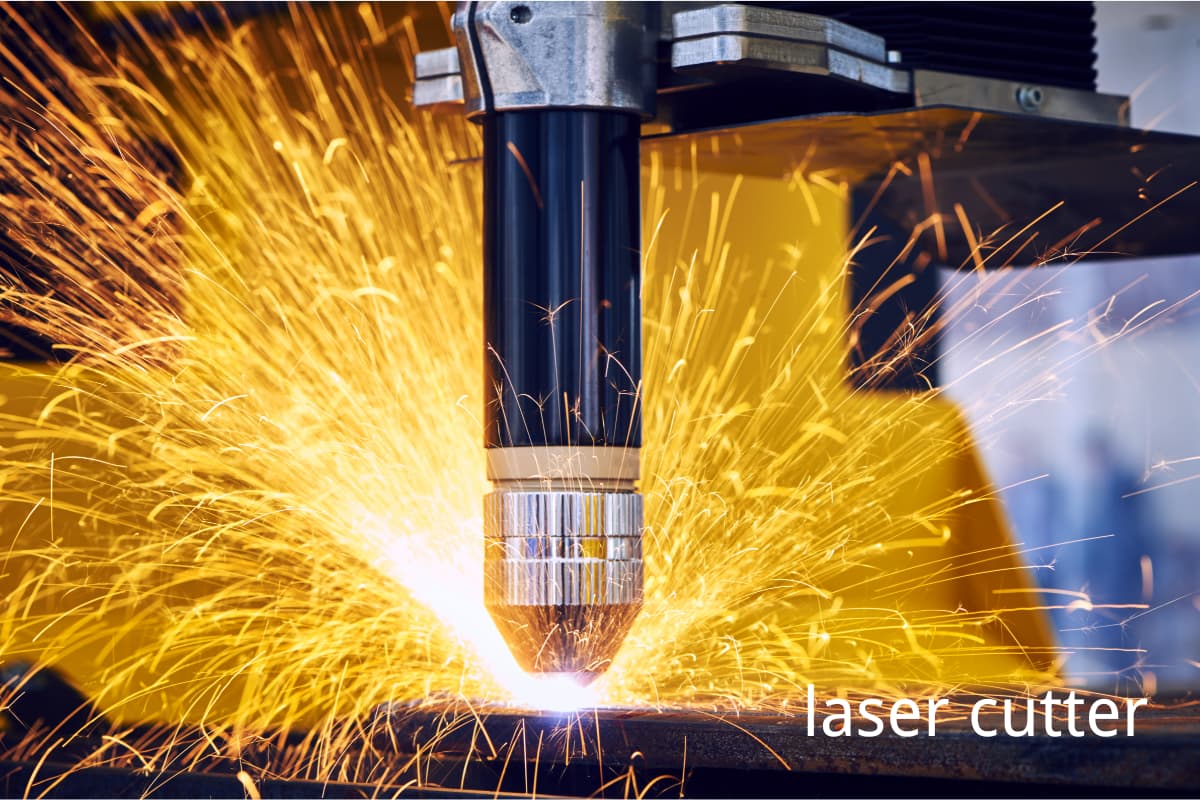

Using a laser-cutting machine correctly can improve processing efficiency and product quality, prolong the product lifespan, and lower maintenance costs. On the contrary, improper operation may damage machines, decrease processing quality and even lead to safety incidents.
Thus, it’s vital for the operators and business managers to have a deep understanding of laser cutting machines’ working principles, operation procedures, safety precautions and maintenance.
The article aims to provide a thorough and detailed user guide on laser-cutting machines. Based on the guide, readers will acquire the basic knowledge, operation procedures and advanced tips and tricks.
No matter you are a beginner or a sofisticated operator, the article can provide you with valuable information to improve the efficiency and safety of laser cutting machine utilization.
II. What is a Laser Cutting Machine?
To learn and understand a laser cutting machine, we should answer three questions: What’s a laser cutting machine, and how does it work? How many types of laser cutting machines are there according to lasers? What’s the application of laser cutting machines in various industries?
1. Definition and basic components
(1)Definition
The laser cutting machine is a piece of equipment that utilizes high-power density laser beams to cut, engrave, and punch.
Its working principle is that the laser beams generated by the generator irradiate the surface of workpieces so as to melt, evaporate, and burn the material's surface layer. At the same time, after the high-pressure gas blows away the molten material, the cutting is finished.
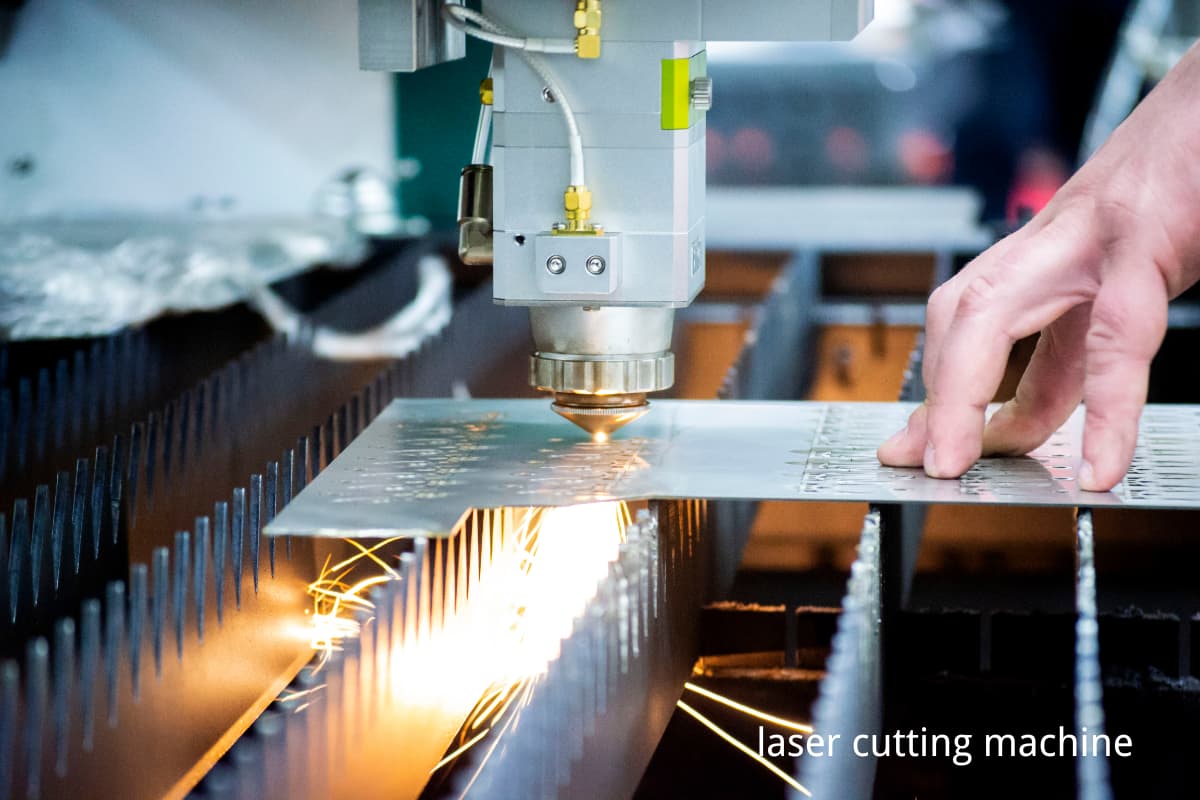

(2)Basic components
A laser cutting machine is mainly composed by the following parts:
- Laser: a core part to generate laser beams
- Optical system: it includes reflective mirrors and focusing lenses for transmitting and focusing laser beams.
- CNC control system: it controls the movements and processing parameters of a laser cutting machine.

- Workbench: it’s used to place and fix the material to be processed.
- Cooling system: it cools the laser generator and optical system to pervent overheating.

According to laser types, the laser types of laser cutting machines can be divided into CO2 laser cutting machines, fiber laser cutting machines, and YAG laser cutting machines.
- Smoke Exhaust System: eliminates smoke and waste gas produced during the processing, maintaining a clean working environment.
2. Types of laser cutting machines (CO2, Fiber, Nd:YAG)
(1)CO2 laser cutting machines
It utilizes CO2 gases as a laser medium, suiting for non-metal material cutting and some metal material cutting.
(2)Fiber laser cutting machines
Utilizing fiber as a laser medium, it boasts high efficiency, energy savings and low maintenance costs, suitable for various metal materials.

(3)YAG laser cutting machine
It utilizes neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet crystal as a laser medium, suitable for high-precise and exquisite processing.
(4)Comparison
This table provides a comprehensive comparison of the three types of laser cutting machines, highlighting their key features, advantages, and disadvantages.
| Feature/Aspect | CO2 Laser Cutting Machine | Fiber Laser Cutting Machine | Nd:YAG Laser Cutting Machine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Medium | CO2 gas | Optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements | Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (Nd:YAG) |
| Wavelength | 10.6 micrometers | 1.064 micrometers | 1.064 micrometers |
| Material Suitability | Non-metals (wood, acrylic, plastic), some metals | Metals (steel, aluminum, copper, brass) | Metals, ceramics, some plastics |
| Cutting Speed | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Cutting Thickness | Suitable for thicker materials | Best for thin to medium-thickness materials | Suitable for thin to medium-thickness materials |
| Beam Quality | Good | Excellent | Good |
| Efficiency | Lower (10-20%) | Higher (25-30%) | Moderate |
| Maintenance Requirements | Higher (requires regular maintenance of optics) | Lower (solid-state, fewer moving parts) | Moderate (requires maintenance of flash lamps) |
| Initial Cost | Moderate | Higher | High |
| Operating Cost | Higher (consumables like gas, optics maintenance) | Lower (less consumables, higher efficiency) | Moderate |
| Lifespan of Laser Source | 8,000-15,000 hours | 50,000-100,000 hours | 8,000-15,000 hours |
| Cooling Requirements | Requires water cooling | Air or water cooling | Requires water cooling |
| Applications | Signage, woodworking, plastics, textiles | Automotive, aerospace, electronics, metalworking | Medical devices, precision engineering, jewelry |
| Advantages | Versatile, good for non-metals, lower initial cost | High efficiency, low maintenance, excellent for metals | High precision, good for both metals and non-metals |
| Disadvantages | Higher operating cost, lower efficiency | Higher initial cost, best for metals | High initial and operating costs, moderate efficiency |
Further, I’d like to share you a simpler table to have an even more intuitive comparison.
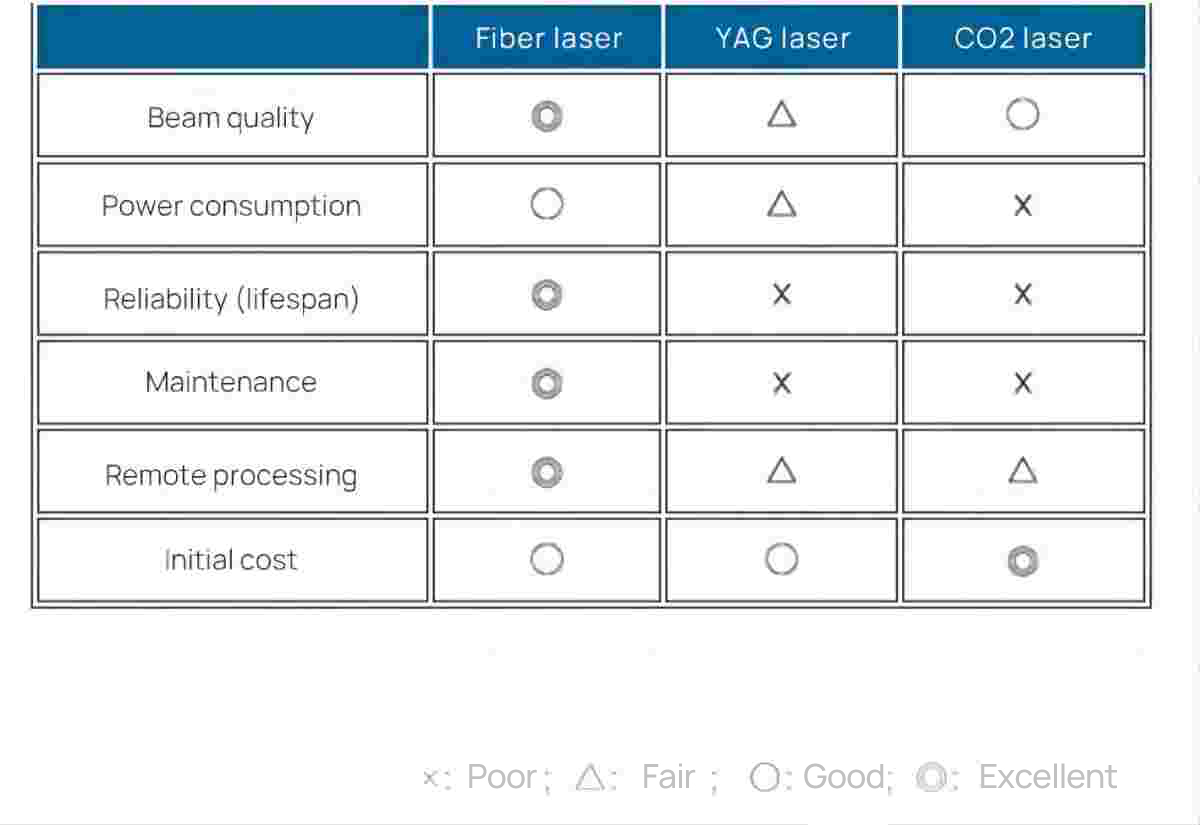
3. Applications in various industries
Generally, laser cutting machines are widely applied in many sectors.
(1) Metal processing
They can cut stain steel, stainless steel and aluminum alloy and are suitable for mechanical manufacturing and sheet metal processing.
(2) Electronic fabrication
They can cut circuit boards and electronic components, so they are suitable for electronic product production and assembly.
(3) Automotive industry
They are capable of cutting vehicle components and body parts to improve production efficiency and product quality.
(4) Aerospace
They are used for cutting aerospace materials and meet high speed and strength processing requirements.
(5) Advertising
They can cut acrylic, wood and plastic for the production of billboards and signs.

III. Step-by-Step Guide to Use a Laser Cutting Machine
Let's view a short video!
Step 1: Preparing the Material
(1)Types of materials suitable for laser cutting
Laser cutting machines can cut all kinds of materials, including metal and non-metal materials. Commonly, here are some materials suitable for laser cutting:
- Metal materials: stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, copper and brass.
- Non-materials: wood, acrylic, plastic, leather, paper and cloth.


(2)Material preparation tips
- Clean material surface: ensure the material surface is free of oil stains, dust, and other impurities to guarantee cutting quality.
- Check material thickness: choose appropriate laser power and cutting speed based on material thickness.
- Fix material: ensure the materials’ stationary to minimize cutting errors.
Step 2: Loading the Material
(1)Proper placement and securing
- Flat placement: Place the materials flatly on the workbench to guarantee a parallel between the material surface and the cutting head.
- Fix material: use clamps, magnets and other tools to fix materials so as to prevent material from moving during cutting.

(2)Adjusting the laser head
- Height Adjustment: adjust the height of the laser head according to the material thickness, guaranteeing that the laser beam is focused on the material surface.
- Calibration of the cutting path: ensure the cutting head moves along the cutting path so as to avoid cutting errors.
Step 3: Configuring the Machine Settings
(1)Power and speed settings
- Laser power: the selection of laser power should be based on material types and thicknesses. Generally, thicker materials entail higher power.
- Cutting speed: the selection of cutting speed should be based on material types and cutting requirements. Higher cutting speeds are suitable for thinner materials and lower speeds for thicker materials.
(2)Focus and alignment
- Focal length adjustment: ensure lasers are focused on the material surfaces to optimize cutting performance.
- Cutting path alignment: use alignment tools or software to ensure the laser head is accurately aligned with the cutting path.
Step 4: Running a Test Cut
(1)Importance of test cuts
- Verification settings: verify whether the laser power, cutting speed and focal length settings are appropriate through test cutting.
- Check cutting quality: conduct tests to check whether the cut edges are smooth and free of burrs, and if the cutting depth meets the requirements.
(2)Analyzing test results and adjustments
- Test results analysis: analyze cutting quality and performance based on cutting results
- Adjust settings: adjust laser powers, cutting speed and focal lengths according to analysis results so as to ensure cutting quality.
Step 5: Executing the Final Cut
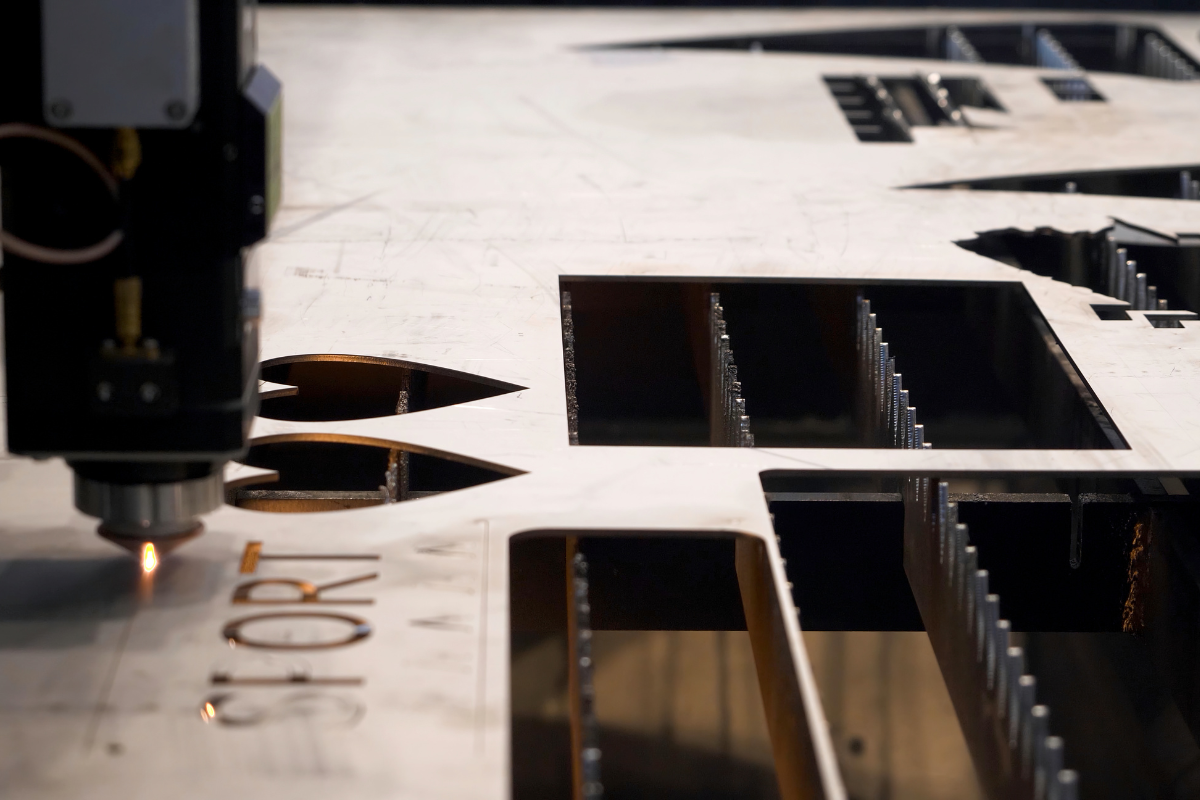

(1)Monitoring the cutting process
- Real-time inspection: the operation state of a laser cutting machine should be inspected during cutting to guarantee the cutting process.
- Handling exceptions: If anomalies are detected, such as cutting deviations or material movement, promptly pause the cutting and make adjustments.
(2)Post-cut inspection and adjustments
- Check cutting quality: after cutting, check if the cutting edges are smooth and free from burrs and if the cutting depth meets the requirements.
- Necessary post-cutting processing: remove burrs, clean the cut surfaces, etc., to ensure the final product quality.
Based on the step-by-step operation guides above, operators and beginners can use laser cutting machines correctly and safely and guarantee cutting performance and efficiency.
VI. Advanced Tips and Tricks
1. Optimizing Cutting Speed and Quality
Speed and precision are two key factors during the cutting process. To maximize cutting results, a balance between speed and precision should be achieved during cutting.
(1)Balancing speed and precision
- Adjust laser power
Laser power directly affects cutting speed and quality. High power improves cutting speed, but decreases cutting edge smoothness.
On the contrary, low power improves cutting precision but decreases cutting speed. Therefore, proper laser power adjustment according to material thickness and type is vital.
- Choose the proper focal length
The focal length determines the location of laser beam’s focal point. Appropriate focal length can ensure that laser beams form a small spot on the material surface so as to improve cutting precision. Normally, shorter focal lengths suit thinner materials while longer ones for thicker.

- Optimize cutting paths
The proper cutting paths can reduce the movement distance of a cutting head, improving cutting efficiency. CAD software-designed cutting paths should avoid unnecessary turns and repeatitive cutting.
- Use assist gas
Assist gases, such as oxygen, nitrogen or air, can help clean the molten during cutting, improving cutting quality. Different materials entail different assist gases. For example, oxygen suits carbon steel cutting while nitrogen suits stainless steel and aluminum cutting.
(2)Cutting Techniques for Different Materials
Different materials present different features, which needs to adopt different cutting techniques
- Metal materials
This table provides a detailed reference for the choice of assist gas, the function of the assist gas, laser power, cutting speed, and other considerations for cutting different metal materials with a laser.
| Metal Material | Assist Gas | Assist Gas Function | Laser Power | Cutting Speed | Other Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Oxygen | Reacts with carbon steel to produce high temperature, increasing cutting speed | Medium to High | Medium | Control laser power and cutting speed to avoid excessive melting |
| Stainless Steel | Nitrogen | Prevents surface oxidation, maintains smooth cutting edges | High | Slow | Ensure cutting quality, avoid edge oxidation |
| Aluminum | Nitrogen or Air | Prevents oxidation, adapts to high reflectivity | High | Medium | Pay special attention to laser beam focusing to prevent reflection damage to the laser |


- Non-metal materials
This table provides a quick reference for the choice of assist gas, laser power, cutting speed, and key considerations when laser cutting various non-metal materials.
| Non-Metal Material | Assist Gas | Laser Power | Cutting Speed | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Air | Low | Fast | Avoid excessive burning |
| Acrylic | Air or Nitrogen | Medium | Medium | Ensure smooth cutting edges |
| Fabric | Air | Low | Fast | Avoid melting or burning |
This table provides a quick reference for the choice of assist gas, laser power, cutting speed, and key considerations when laser cutting various non-metal materials.
2.Creative Uses of Laser Cutting
(1)Custom designs and projects
Laser-cutting technology is not only widely applied in industrial manufacturing but presents significant potential in creative and customized projects.
- Customized furniture
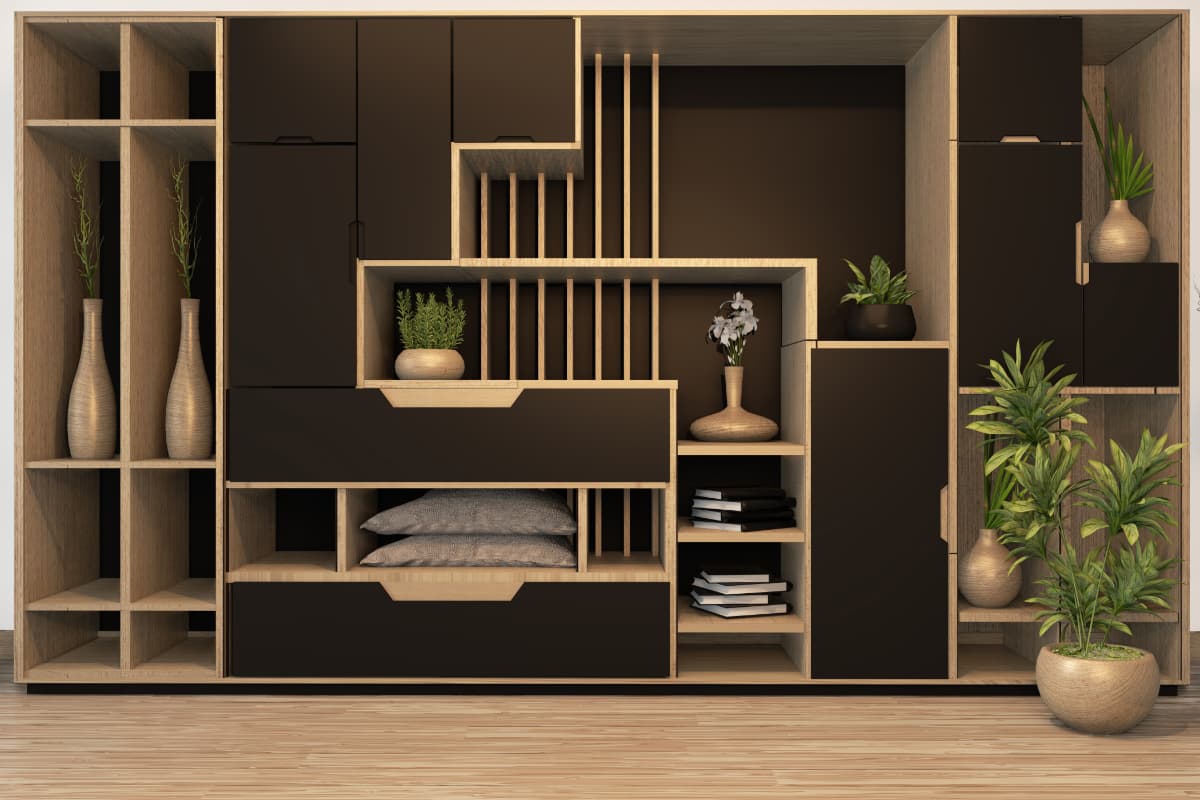

Laser cutters can cut wood, metal and acrylic precisely and allow for personalized furniture design. Designers can make intricate patterns and structures using laser cutting machines to provide personalized furniture design service.
- Artwork production
Laser cutters can make exquisite artworks, such as Such as carvings, decorations, and lighting fixtures, etc. Artists can cut precise patterns and details and make unique artworks.
- Model making
Laser cutting can be used to make construction, mechanical, and tool models. The technology allows each part to be cut precisely and assembled quickly.

(2)Business opportunities
Laser-cutting technology brings about many commercial opportunities. Here are business opportunities you can explore with the help of laser cutting machines.
- Customized product service
You can provide customized products, such as customized furniture, gifts and decorations. Laser cutting technology can meet personalized demands and provide high-quality customized profucts.
- Small batches of production
Laser cutting technology suits small batches of production and can quick response to market demands. Enterprises can use laser cutting machine technology to carry out small batches of production, lower production costs and improve product efficiency.
- Creative studio
Open a creative studio, provide laser cutting equipment and technical support for designers, artists and makers. The creative studio can become an innovative platform for laser cutting technology, promoting the combination of creative design and technical application.
In summary, laser cutting technology not only plays a significant role in industrial manufacturing but also demonstrates enormous potential in creative design and commercial applications.

By continuously optimizing cutting speed and quality, exploring creative applications of laser cutting can achieve more efficient and precise cutting effects, opening up more business opportunities.
V. Conclusion
According to the step by step guide for laser cutters’ users, you can start a journey of exploring laser cutting technology.
ADH Machine Tool offers a variety of top-tier laser cutting machines to meet all your cutting needs. Our dual-use fiber laser cutting machines (ULFT and ULET) can not only cut sheet metal, but also tubes with diameters from 20-320mm, satisfying diverse processing requirements.

For customers who require high precision cutting, our precision laser cutter (ULJM) is specifically designed for cutting non-ferrous metals such as copper, nickel, cobalt and precious metals like gold, silver and platinum with a thickness range of 0.1-4mm.
Choose ADH laser cutters for exceptional performance and reliable quality that will boost your business. Contact our professional sales team now for a free quote and more information!
Green Fodder Shredder,Small Domestic Green Fodder Chopper,Thickened Green Fodder Chopper,Four Knife Green Fodder Chopper
Hunan Nongle Machinery Co., Ltd. , https://www.nongleagro.com
